Co-management of Patients With PAH-CTD
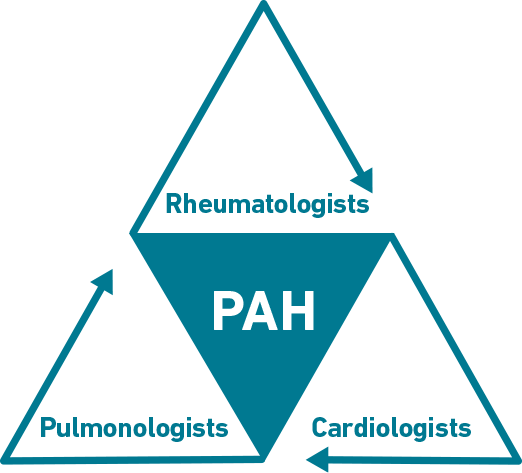
Rheumatologists are integral to the detection and co-management of PAH associated with systemic sclerosis (PAH-SSc). The identification, diagnosis, and management of PAH-SSc requires collaboration among pulmonologists, cardiologists, and rheumatologists.1,2 Given the complex nature of PAH and its diagnosis and management, it is important to consider partnering with specialists who have experience in managing this condition.2-4
PARTNERSHIP of PAH-SSc specialists
Referral
Utilizing the Pulmonary Hypertension Association’s network of Centers of Comprehensive Care and Regional Clinical Programs to collaborate with appropriate specialists may reduce PAH-SSc diagnosis delay and improve outcomes.6
Confirming a PAH diagnosis7
- An RHC is required to confirm a diagnosis
- The 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines recommend that an RHC be performed in a PH center
Treatment Pathways in PAH
Early diagnosis and treatment may improve long-term outcomes in PAH7-9
- The goal of PAH treatment is to achieve and maintain a low-risk status7
- A risk assessment should be performed at diagnosis and follow-up7
- A low-risk status at diagnosis focuses on WHO FC I or II, 6MWD >440 m, BNP <50 ng/L, NT-proBNP <300 ng/L, RAP <8 mmHg, CI ≥2.5 L/min/m2, SVI >38 mL/m2, and SvO2 >65%*
- A low-risk status at follow-up includes WHO FC I or II, 6MWD >440 m, BNP <50 ng/L, or NT-proBNP <300 ng/L
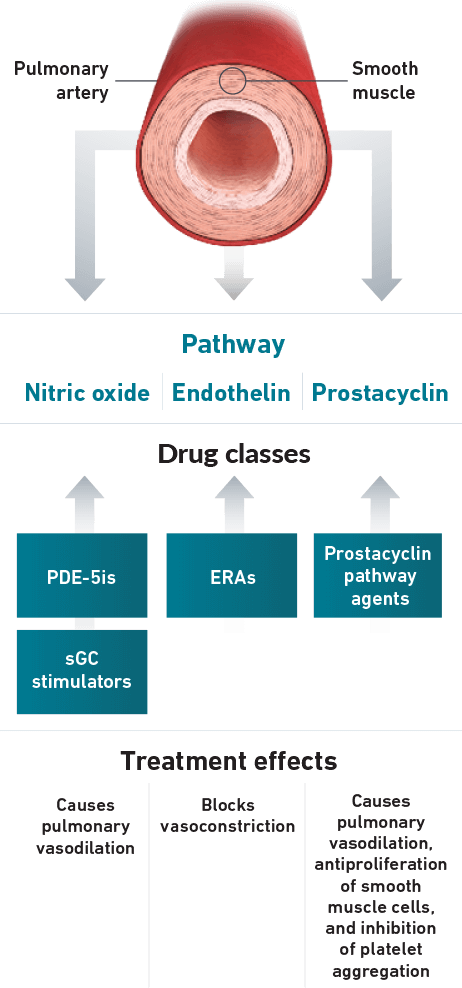
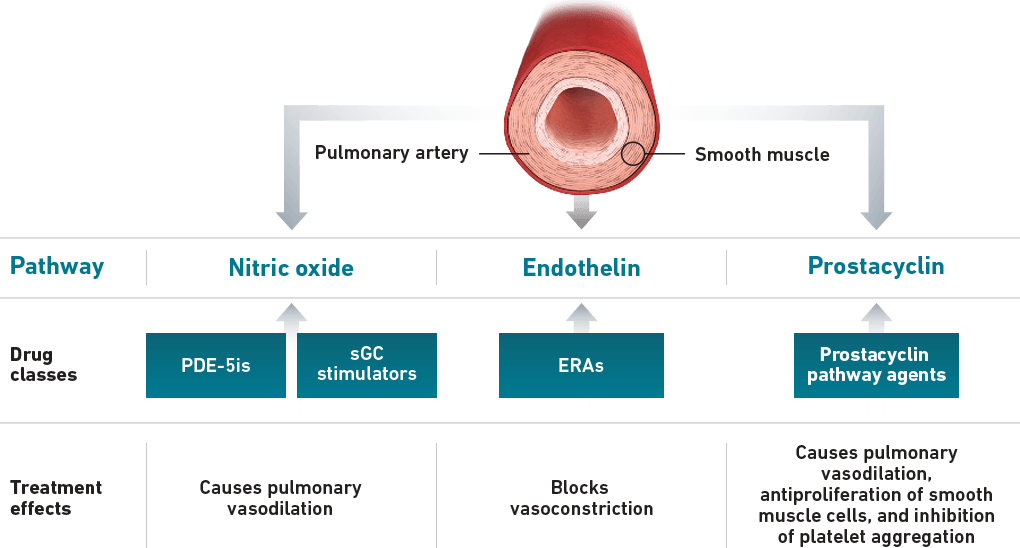
Guidelines recognize that focusing on multiple pathways is an effective treatment strategy7
- 3 separate signaling pathways in PAH can be targeted by different drug classes7,10:
Nitric Oxide Pathway (PDE-5is and sGC stimulators)7,10
Endothelin Pathway (ERAs)7,10
Prostacyclin Pathway (Prostacyclin pathway agents)7,10
disease progression7,9
