PAH-SSc Findings
DETECT was a large, international, prospective, cross-sectional study funded and supported by Actelion Pharmaceuticals Ltd.1
About the DETECT study1:
- Objective was to develop an algorithm to help assess for risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), or scleroderma, to optimize diagnostic right heart catheterization (RHC) and minimize missed PAH diagnoses
- Included patients with SSc who were ≥18 years old with a diagnosis of SSc of >3 years' duration from first non-Raynaud's symptom
- Sixty-two experienced centers across 18 countries/territories performed RHCs on 466 patients with SSc at increased risk for PAH*
PAH-SSc WAS FOUND TO BE MUCH MORE COMMON THAN PREVIOUS STUDIES HAVE SUGGESTED1-3
Nearly 1 in 5 patients with SSc (19%, 87/466) were found to have associated PAH via RHC1
SCREENING OF PATIENTS WITH NONSYMPTOMATIC SSc MAY HELP EARLY DIAGNOSIS
PAH was mild in nearly two-thirds of patients with PAH-SSc (64%, 56/87): WHO FC I/II with moderately elevated mPAP, pulmonary vascular resistance, and preserved mean cardiac index1
PAH-SSc CAN PROGRESS QUICKLY
44% (25/57) of patients with PAH-SSc with follow-up data progressed during a short time (median observation time,
12.6 months)4†


For more details about the DETECT study, read the publication from the Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
prevalent form of PAH in the US and Europe.5 Learn More About How Many People Are Living With PAH-CTD Today >
DETECT Algorithm
The 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for PH gave the DETECT algorithm the highest class recommendation (Class I) to identify asymptomatic patients with PAH in those with SSc of >3 years’ disease duration, an FVC ≥40%, and a Dlco <60%.5
From 112 initial variables, 13 were selected based on their discriminatory ability to detect PAH and these variables formed the basis of the detection algorithm. Multivariable analysis resulted in 8 measures that together aid in the referral to RHC to identify PAH-SSc, even in patients with milder symptoms, while reducing missed diagnoses and unnecessary testing.1
THE DETECT ALGORITHM 2-STEP DECISION TREE1
Step 1
variables
POINTS >300
- FVC % predicted/Dlco % predicted
- Current/past telangiectasias
- Serum anticentromere antibodies
- Serum NT-proBNP
- Serum urate
- Right-axis deviation on electrocardiogram
POINTS >300
Step 2
POINTS >35
- Right atrium area
- TR velocity
POINTS >35

Referral
for RHC
The DETECT algorithm had a 4% (n=3) rate of missed PAH diagnoses compared with 29% (n=24) using the 2009 ESC/ERS Guidelines.1
- Sensitivity and specificity analyses using the 408 SSc patients in the DETECT study (87 with RHC-confirmed PAH and 321 without)
- Exclusion of any single variable from the DETECT algorithm had only a small impact on model performance. If more than one variable is missing, the model cannot be used reliably‡
DETECT Video
Play the video below to learn how the DETECT screening tool helps identify patients with SSc who should be evaluated for PAH.
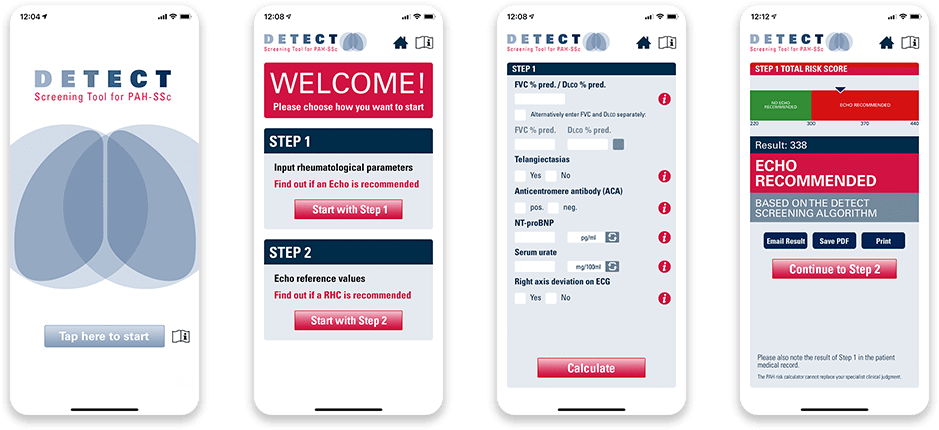
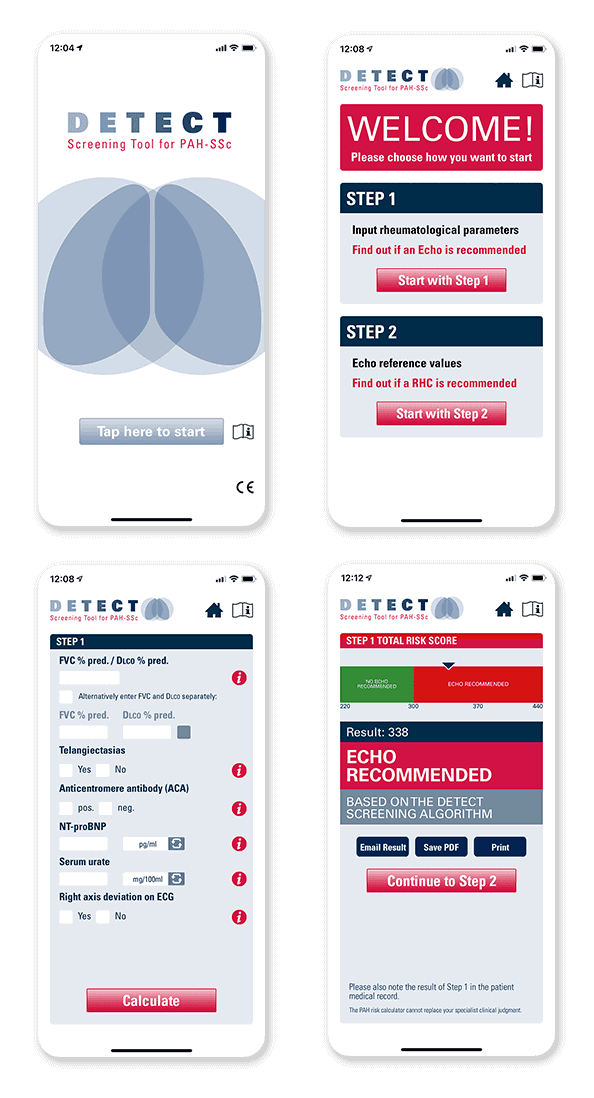
DETECT Screening Tool for PAH-SSc
The DETECT Screening Tool for PAH-SSc using the algorithm developed by Actelion Pharmaceuticals US, Inc., a Janssen Pharmaceutical Company, and validated in the DETECT study is available for download to your iPhone and Android devices. It can help you identify patients with SSc who should be evaluated for PAH using electrocardiography and may be in need of an RHC for confirmation of PAH-SSc.
The DETECT Screening Tool for PAH-SSc is limited for use by healthcare specialists who treat patients with SSc, and who are familiar with PAH as a complication of SSc. It is not intended to replace the medical or professional judgment of healthcare providers. It does not provide professional advice and should not be considered a diagnosis. Healthcare professionals using the tool should exercise clinical judgment as to the information they provide to the patient based upon the tool.
App Store, the Apple logo, and iPhone are trademarks of Apple Inc. Google Play and the Google Play logo are trademarks of Google LLC.


